Getting Started with DeepData
Dashboard Overview
Once connected, the system will display available databases and tables based on the selected sources. Users can drag and drop tables/collections onto the dashboard. Each data source has a unique color for easy identification.
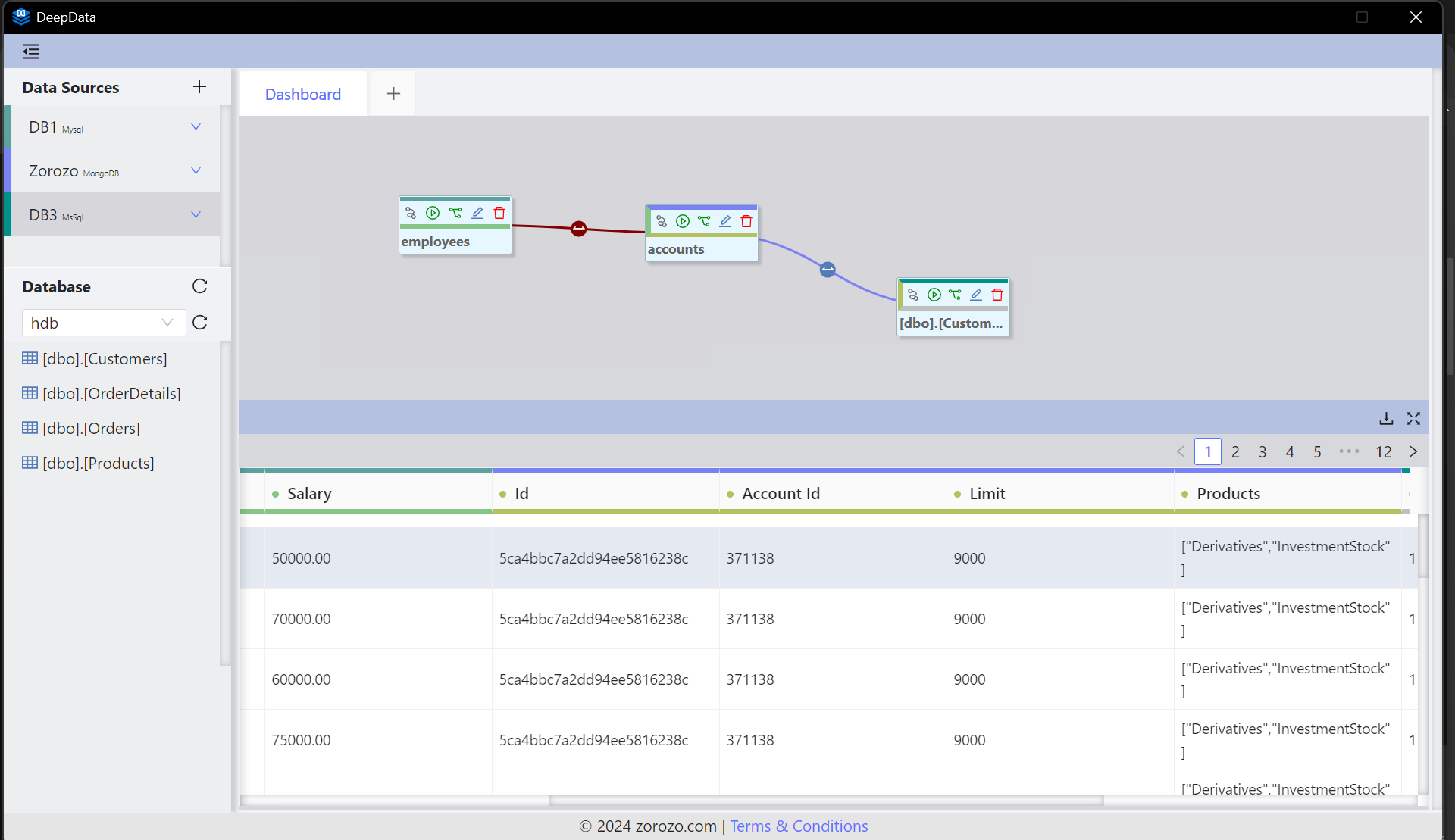
Table Linking and Join Configuration
Users can link tables by dragging connections between them. Child nodes will inherit the parent’s left-border color for clear identification. After linking, users can configure join details.
For normal keys, users can enter the key name directly in the join configuration. However, when dealing with JSON objects, dot notation should be used to reference nested fields.
Example: If there is a key transactions which contains an array, and the first index (0) has a key named amount, the full key reference in a join would be:
transactions.0.amount
Another example: If a key docs contains an array and the first index (0) has a key named fileId, the full key reference in a join would be:
docs.0.fileId
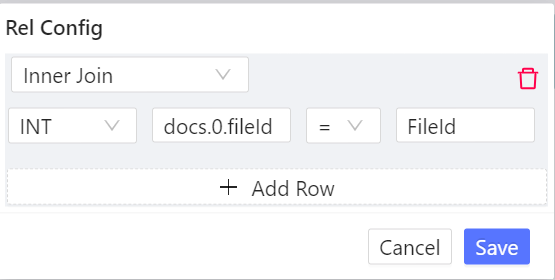
Action Buttons
Each node offers multiple actions:
- Linking
- Execute standalone
- Execute with linked nodes
- Edit query
- Delete
Using ObjectId in MongoDB Queries
When querying MongoDB collections in DeepData, you must properly format ObjectId values. Use the following syntax:
{
"_id": "ObjectId('67713e78b6c927089cc2603c')"
}
Examples
Find a document by _id:
{
"_id": "ObjectId('65f2b07e3d2a4b6d5a9e1234')"
}
Query with additional filters:
{
"_id": "ObjectId('65f2b07e3d2a4b6d5a9e1234')",
"status": "active"
}
Using $in for multiple ObjectIds:
{
"_id": {
"$in": [
"ObjectId('65f2b07e3d2a4b6d5a9e1234')",
"ObjectId('65f2b07e3d2a4b6d5a9e5678')"
]
}
}